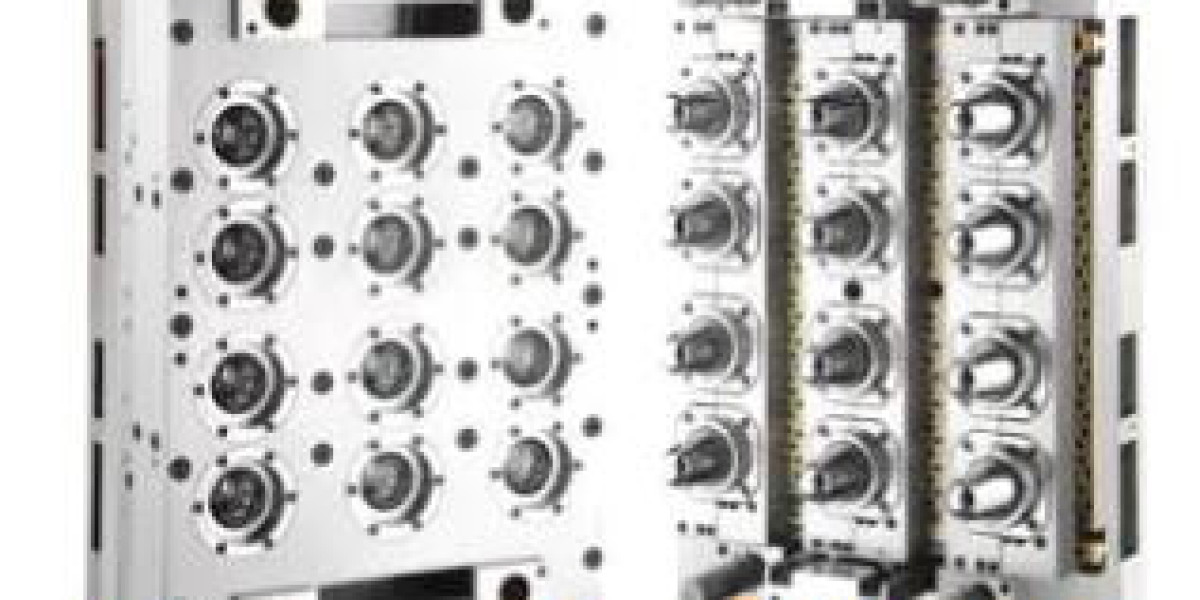
Preform mold are essential in the manufacturing process of various products, particularly in the plastic and glass industries. They are used to shape materials into a specific form before they are further processed or finished. Here's an overview of the functions and types of preform molds:
Functions of Preform Molds
1. Shaping: Preform molds are designed to give a specific shape to the material during the initial stages of production.
2. Consistency: They ensure that each preform is produced with uniform dimensions and quality, which is crucial for subsequent processes.
3. Efficiency: By using molds, the production process can be automated and streamlined, leading to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs.
4. Quality Control: Molds help in maintaining a high level of quality by controlling the shape, size, and surface finish of the preforms.
5. Material Saving: They can be designed to minimize material waste, ensuring that the material is used efficiently.
Types of Preform Molds
1. Injection Molds: These are used in the injection molding process where molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity and then cooled to form the preform.
2. Blow Molds: Commonly used in the production of plastic bottles and containers, blow molds involve inflating a parison (a preheated tube of plastic) into the shape of the mold.
3. Compression Molds: These molds are used for materials that do not flow well, such as thermosetting plastics. The material is placed in the mold, and pressure is applied to shape it.
4. Transfer Molds: Similar to injection molds, but the material is transferred from a heating chamber to the mold cavity under pressure.
5. Thermoforming Molds: Used for creating large, thin-walled parts from plastic sheets. The sheet is heated and then formed over or into the mold.
6. Glass Preform Molds: Specifically designed for the glass industry, these molds are used to shape glass into preforms that will later be blown into bottles or other glassware.
7. Metal Preform Molds: Used in metalworking to shape metal into a preform that can then be used in further manufacturing processes, such as casting.